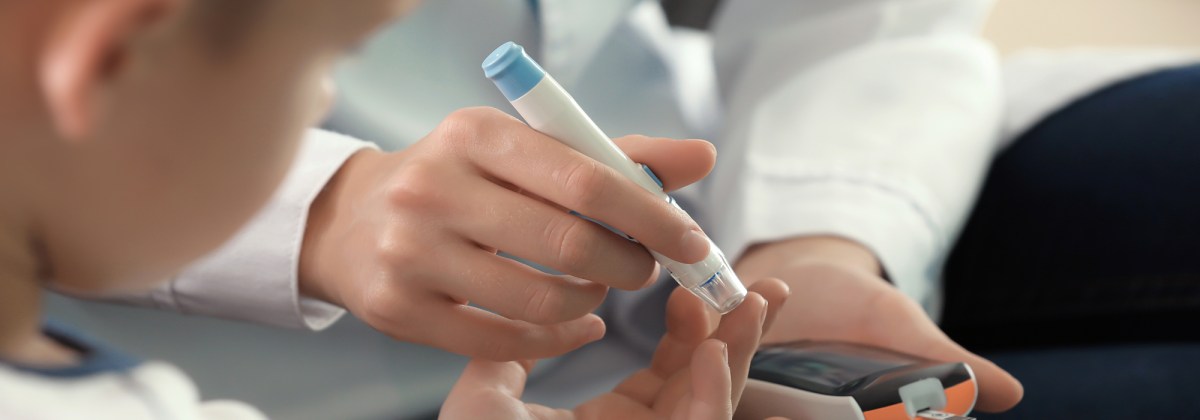
Risk factors for diabetes vary, depending on the type of diabetes.Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults. It was previously known as juvenile diabetes. With type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin. Approximately 5 percent of people with diabetes have type 1 diabetes. With proper insulin therapy, type 1 diabetics can live long, healthy lives.
Check this Article: Penile Implant Surgery in India Cost
The exact cause for type 1 diabetes is unknown. It is often considered to be an autoimmune disorder. An infection or some other unknown trigger causes the body to attack itself, and destroy the cells of the pancreas. Lifetime insulin therapy is necessary. There is no way to prevent type 1 diabetes. Early intervention, and lifelong healthy habits, will reduce the risk of diabetic related complications.
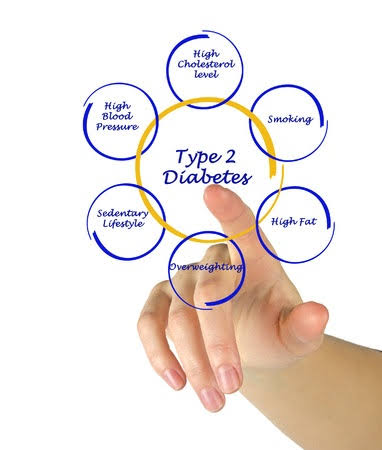
Unlike type 1 diabetes, the symptoms for type 2 diabetes can be more subtle, occurring slowly over a long period of time. A low activity level, a poor diet, and excessive body weight are all risk factors. Many people with type 2 diabetes have these known risk factors and high blood sugars, and are not aware that they have diabetes.
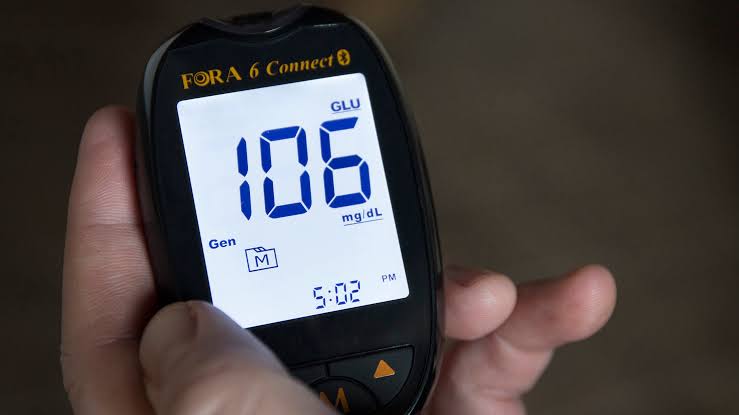
Symptoms for type 2 diabetes can actually include no known symptoms for years. Lack of routine medical care can contribute to people not knowing they are diabetic, all the while suffering the adverse effects of chronically elevated blood glucose levels. Others have symptoms that appear to have no direct link to elevated blood glucose levels, such as frequent infections, poorly healing wounds, and blurred vision and erectile dysfunction. More common symptoms would include the excessive hunger and thirst, fatigue and frequent urination. Blood work is necessary to confirm diabetes; it cannot be diagnosed by symptoms alone.
Gestational diabetes is diabetes that starts or is first diagnosed during a pregnancy. Glucose levels may rise in a pregnant woman due to the changes in hormone levels associated with a pregnancy. Fortunately, the blood glucose levels usually return to normal after the baby is delivered.
Risk factors for gestational diabetes include the following:
- History of hypertension ( high blood pressure)
- History of unexplained stillbirth or miscarriage
- Pre-pregnancy overweight/obesity
- Family history of diabetes
- Previous baby weighing greater than 9 pounds at birth
Early diagnosis and treatment are highly recommended for the health and safety of all individuals diagnosed with diabetes.
Source: http://www.edtreatmentindia.com/